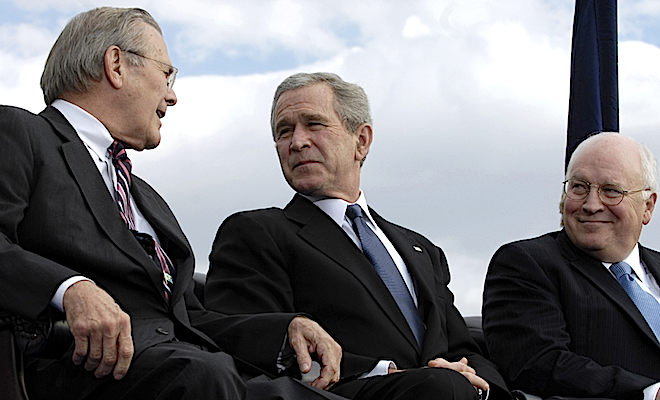
It has frequently been alleged that the modern Turkish Republic operates on two levels. It has a parliamentary democracy complete with a constitution and regular elections, but there also exists a secret government that has been referred to as the“deep state,” in Turkish “Derin Devlet.”
The concept of “deep state” has recently become fashionable to a certain extent, particularly to explain the persistence of traditional political alignments when confronted by the recent revolutions in parts of the Middle East and Eastern Europe. For those who believe in the existence of the deep state, there are a number of institutional as well as extralegal relationships that might suggest its presence.
Some believe that this deep state arose out of a secret NATO operation called “Gladio,” which created an infrastructure for so-called “stay behind operations” if Western Europe were to be overrun by the Soviet Union and its allies. There is a certain logic to that assumption, as a deep state has to be organized around a center of official and publicly accepted power, which means it normally includes senior officials of the police and intelligence services as well as the military. For the police and intelligence agencies, the propensity to operate in secret is a sine qua non for the deep state, as it provides cover for the maintenance of relationships that under other circumstances would be considered suspect or even illegal.
In Turkey, the notion that there has to be an outside force restraining dissent from political norms was, until recently, even given a legal fig leaf through theConstitution of 1982, which granted to the military’s National Security Council authority to intervene in developing political situations to “protect” the state. There have, in fact, been four military coups in Turkey. But deep state goes far beyond those overt interventions. It has been claimed that deep state activities in Turkey are frequently conducted through connivance with politicians who provide cover for the activity, with corporate interests and with criminal groups who can operate across borders and help in the mundane tasks of political corruption, including drug trafficking and money laundering.
A number of senior Turkish politicians have spoken openly of the existence of the deep state. Prime Minister Bulent Ecevit tried to learn more about the organization and, for his pains, endured an assassination attempt in 1977. Tansu Ciller eulogized“those who died for the state and those who killed for the state,” referring to the assassinations of communists and Kurds. There have been several significant exposures of Turkish deep state activities, most notably an automobile accident in 1996 in Susurluk that killed the Deputy Chief of the Istanbul Police and the leader of the Grey Wolves extreme right wing nationalist group. A member of parliament was also in the car and a fake passport was discovered, tying together a criminal group that had operated death squads with a senior security official and an elected member of the legislature. A subsequent investigation determined that the police had been using the criminals to support their operations against leftist groups and other dissidents. Deep state operatives have also been linked to assassinations of a judge, Kurds, leftists, potential state witnesses, and an Armenian journalist. They have also bombed a Kurdish bookstore and the offices of a leading newspaper.
As all governments—sometimes for good reasons—engage in concealment of their more questionable activities, or even resort to out and out deception, one must ask how the deep state differs. While an elected government might sometimes engage in activity that is legally questionable, there is normally some plausible pretext employed to cover up or explain the act.
But for players in the deep state, there is no accountability and no legal limit. Everything is based on self-interest, justified through an assertion of patriotism and the national interest. In Turkey, there is a belief amongst senior officials who consider themselves to be parts of the status in statu that they are guardians of the constitution and the true interests of the nation. In their own minds, they are thereby not bound by the normal rules. Engagement in criminal activity is fine as long as it is done to protect the Turkish people and to covertly address errors made by the citizenry, which can easily be led astray by political fads and charismatic leaders. When things go too far in a certain direction, the deep state steps in to correct course.
And deep state players are to be rewarded for their patriotism. They benefit materially from the criminal activity that they engage in, including protecting Turkey’s role as a conduit for drugs heading to Europe from Central Asia, but more recently involving the movement of weapons and people to and from Syria. This has meant collaborating with groups like ISIS, enabling militants to ignore borders and sell their stolen archeological artifacts while also negotiating deals for the oil from the fields in the areas that they occupy. All the transactions include a large cut for the deep state.
If all this sounds familiar to an American reader, it should, and given some local idiosyncrasies, it invites the question whether the United States of America has its own deep state.
First of all, one should note that for the deep state to be effective, it must be intimately associated with the development or pre-existence of a national security state. There must also be a perception that the nation is in peril, justifying extraordinary measures undertaken by brave patriots to preserve life and property of the citizenry. Those measures are generically conservative in nature, intended to protect the status quo with the implication that change is dangerous.
Those requirements certainly prevail in post 9/11 America, and also feed the other essential component of the deep state: that the intervening should work secretly or at least under the radar. Consider for a moment how Washington operates. There is gridlock in Congress and the legislature opposes nearly everything that the White House supports. Nevertheless, certain things happen seemingly without any discussion: Banks are bailed out and corporate interests are protected by law. Huge multi-year defense contracts are approved. Citizens are assassinated by drones, the public is routinely surveilled, people are imprisoned without be charged, military action against “rogue” regimes is authorized, and whistleblowers are punished with prison. The war crimes committed by U.S. troops and contractors on far-flung battlefields, as well as torture and rendition, are rarely investigated and punishment of any kind is rare. America, the warlike predatory capitalist, might be considered a virtual definition of deep state.
One critic describes deep state as driven by the “Washington Consensus,” a subset of the “American exceptionalism” meme. It is plausible to consider it a post-World War II creation, the end result of the “military industrial complex” that Dwight Eisenhower warned about, but some believe its infrastructure was actually put in place through the passage of the Federal Reserve Act prior to the First World War. Several years after signing the bill, Woodrow Wilson reportedly lamented, “We have come to be one of the worst ruled, one of the most completely controlled and dominated governments in the civilized world, no longer a government by conviction and the vote of the majority, but a government by the opinion and duress of a small group of dominant men.”